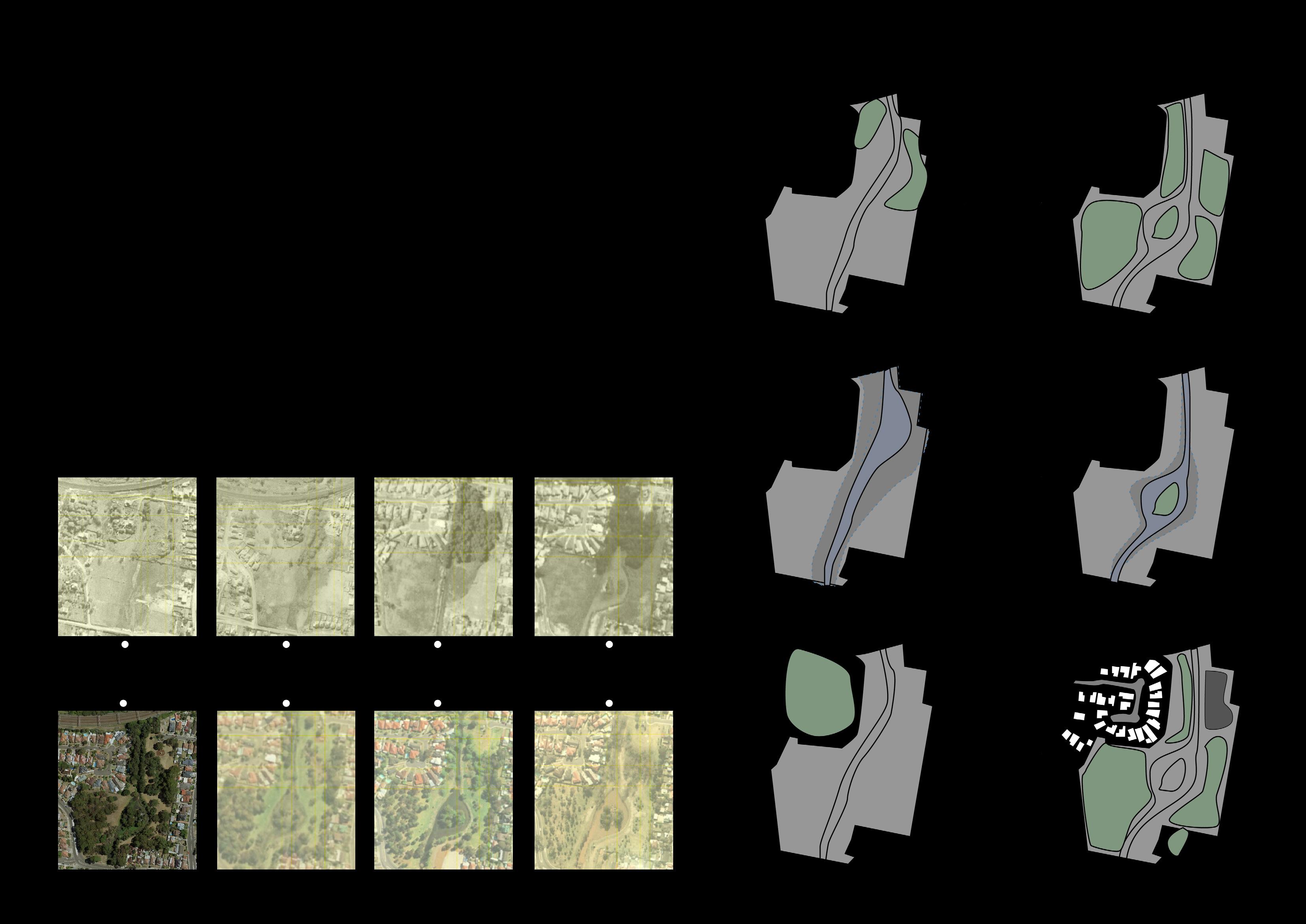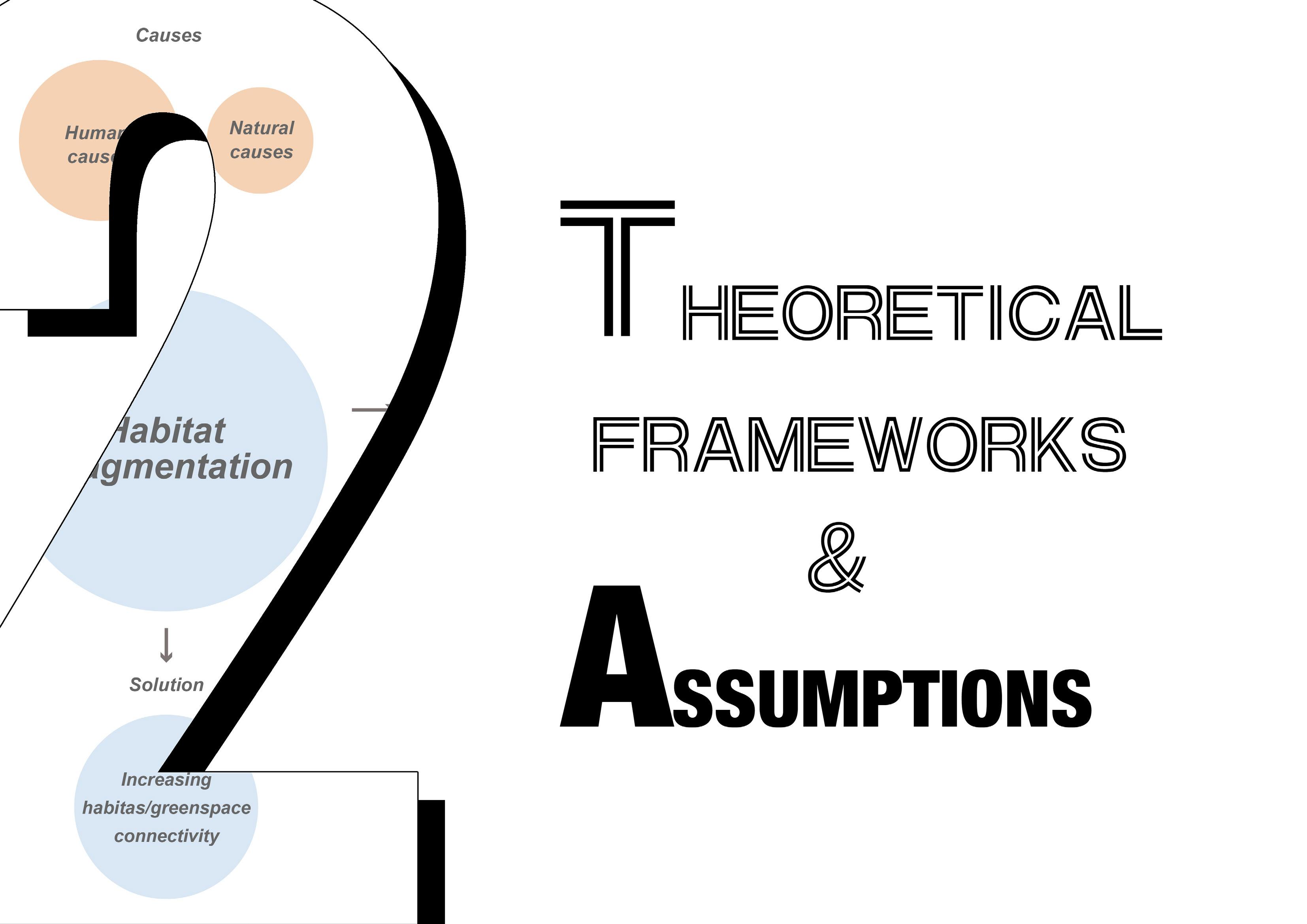



Habitat fragmentation is a ubiquitous landscape pattern in cities, usually accompanied by habitat loss and isolation. Natural causes such as biological invasions and fires may also cause fragmentation of the landscape. However, most of the fragmented landscape changes the land type due to the interference of human behaviour and eventually forms fragmented, island-like landscape fragments (Dramstad, WE, Olson, JD & Forman, 1996, p. 41).
The fragmentation of habitat can help some fields, but excessive fragmentation will only have a negative impact. (Haddad et al., 2015, p.7).
A large amount of experimental data shows that scattered habitats will lead to the continuous deterioration of the ecosystem, reduce the persistence and abundance of species, and reduce the nutrition and other serious environmental problems of the habitat (Haddad et al., 2015, p.5). The fragmentation of habitats will also lead to many climate disasters, such as floods and land areas becoming "oceans".
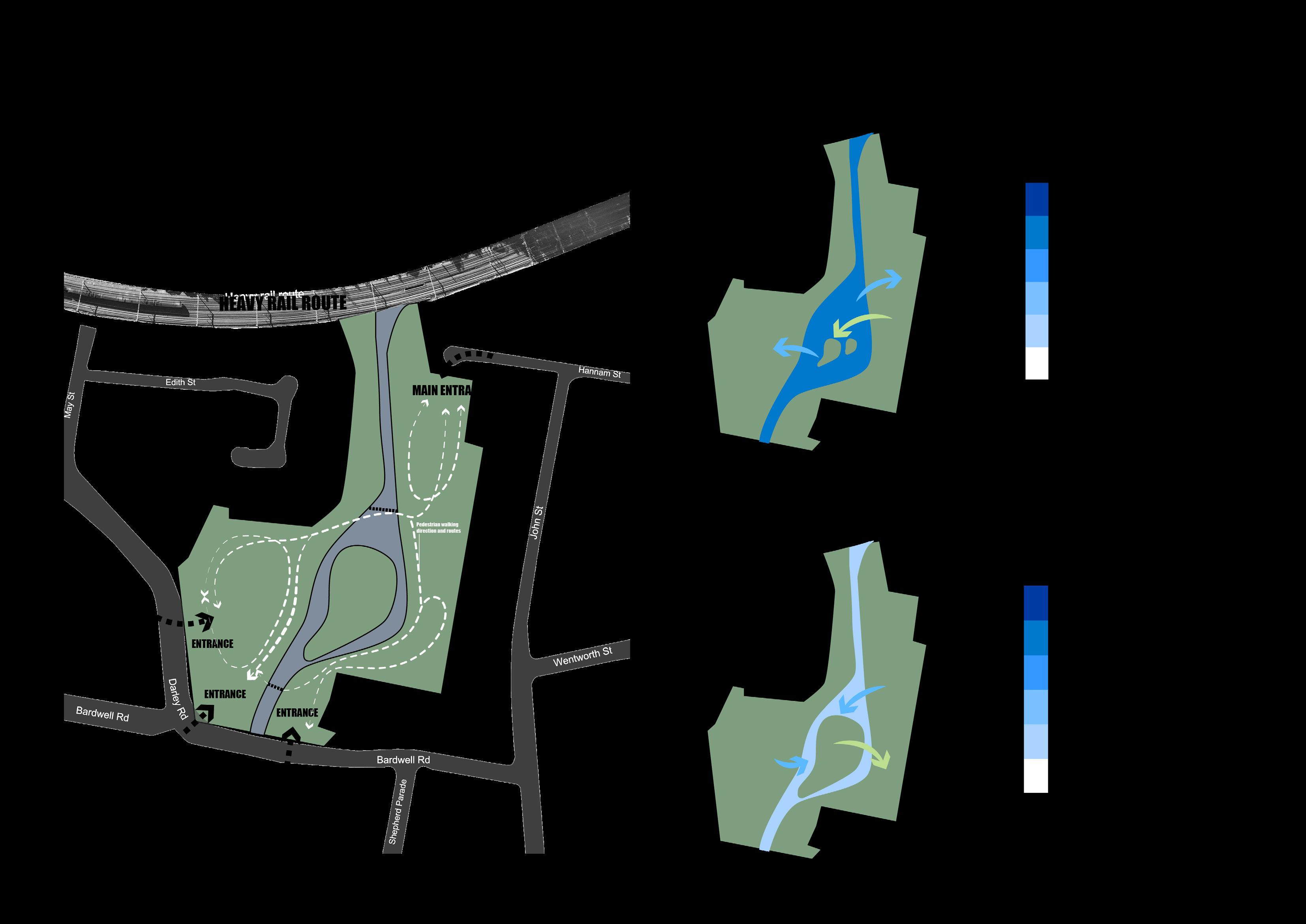
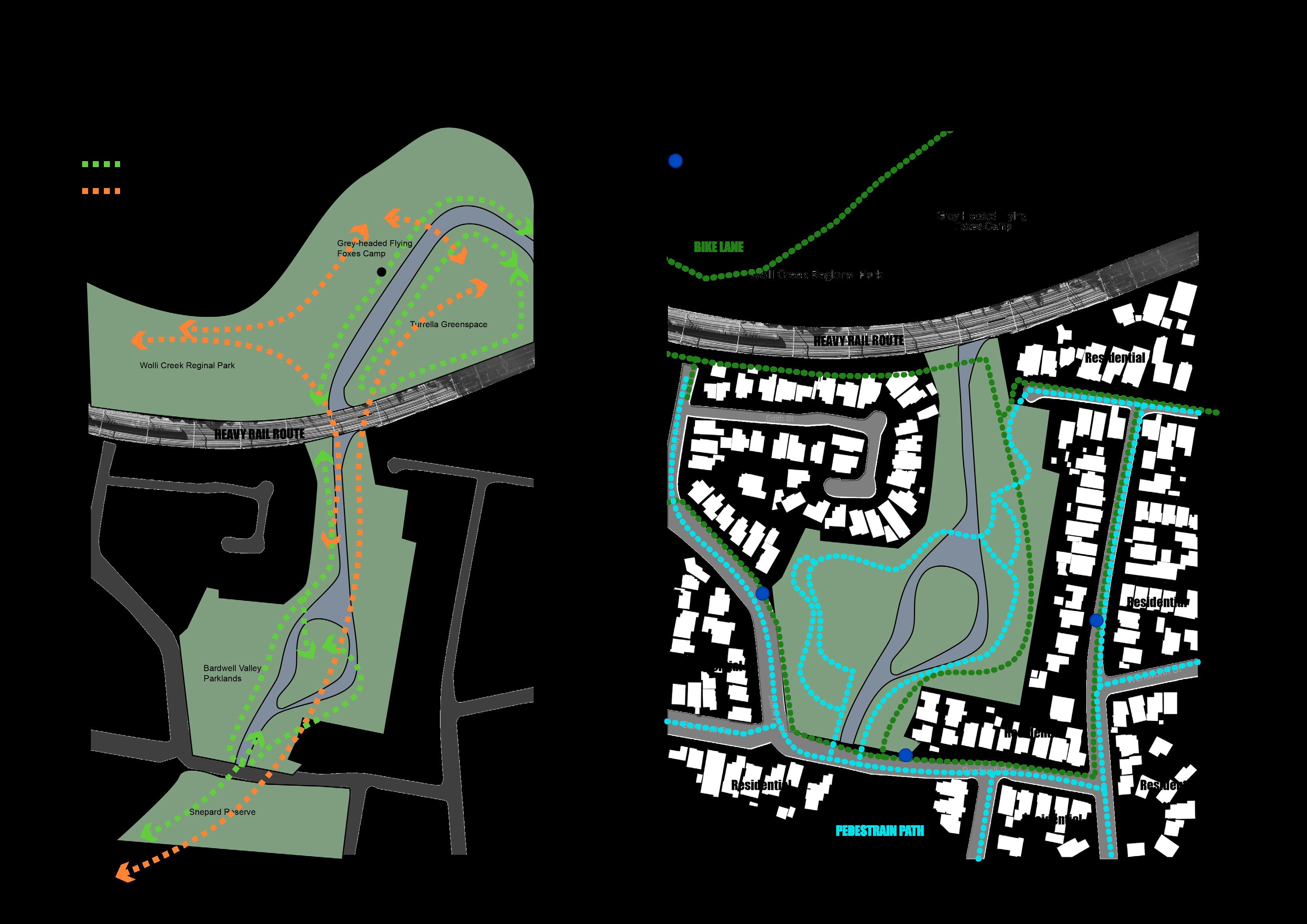
HOW to balance human behaviours and habitat protection and protect and restore the habitat of aquatic animals and plants through increasing habitat connectivity?
1 Frame of Reference
Landscape ecology
Herrington’s book
System theory and cybernetic
The regenerative landscape
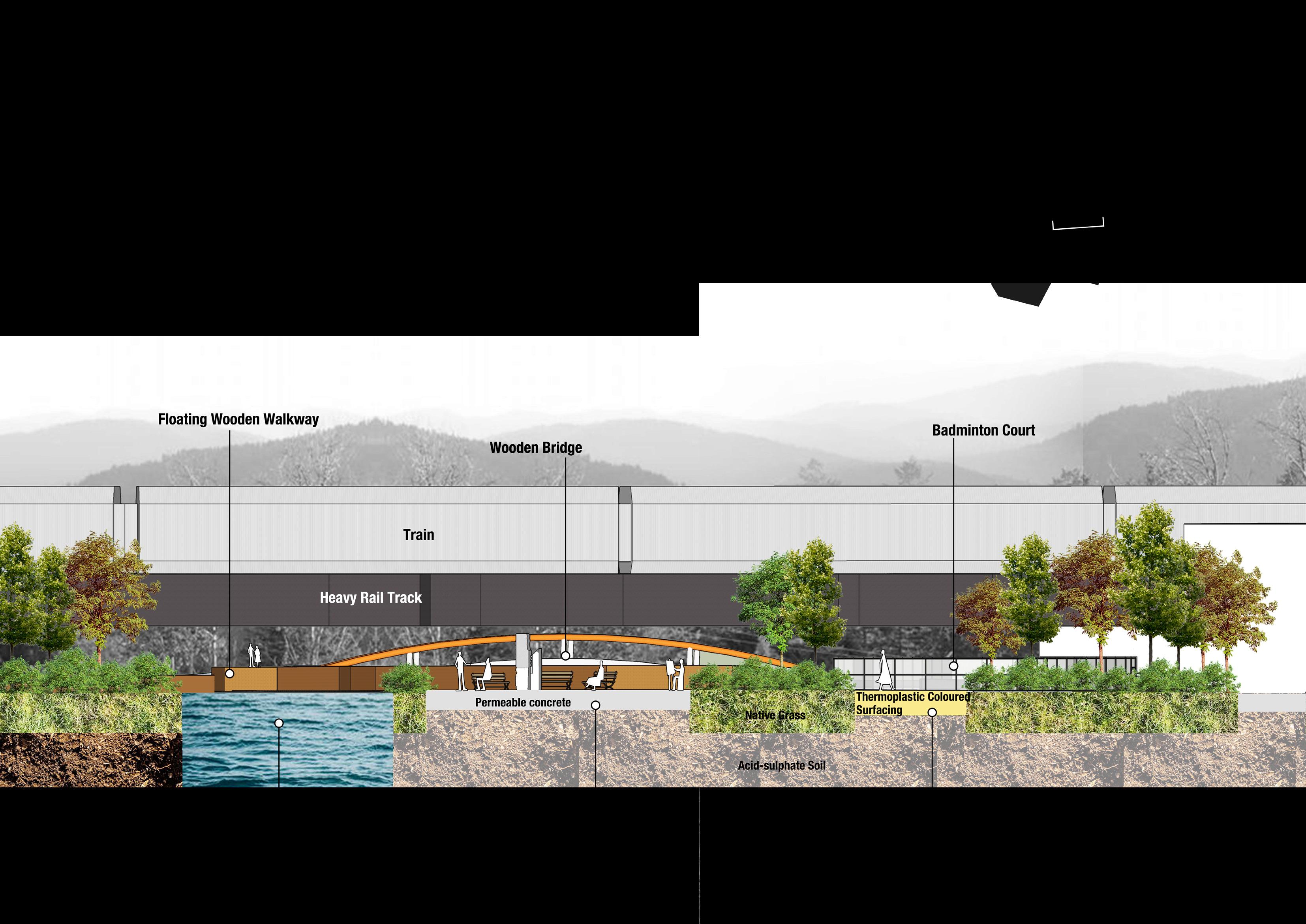
Infrastructure
Green infrastructure
Landscape connectivity
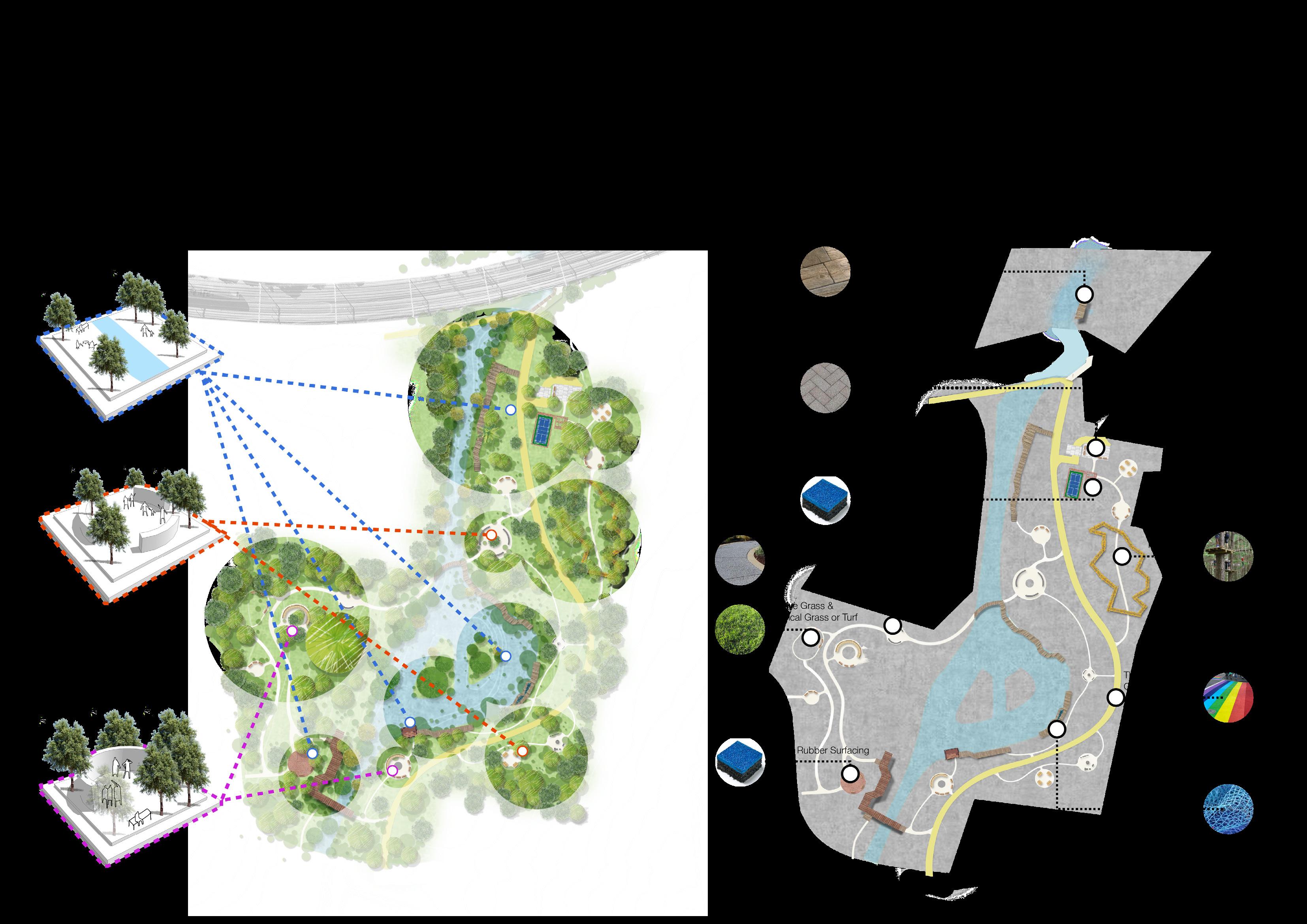
2 Precedents Analysis
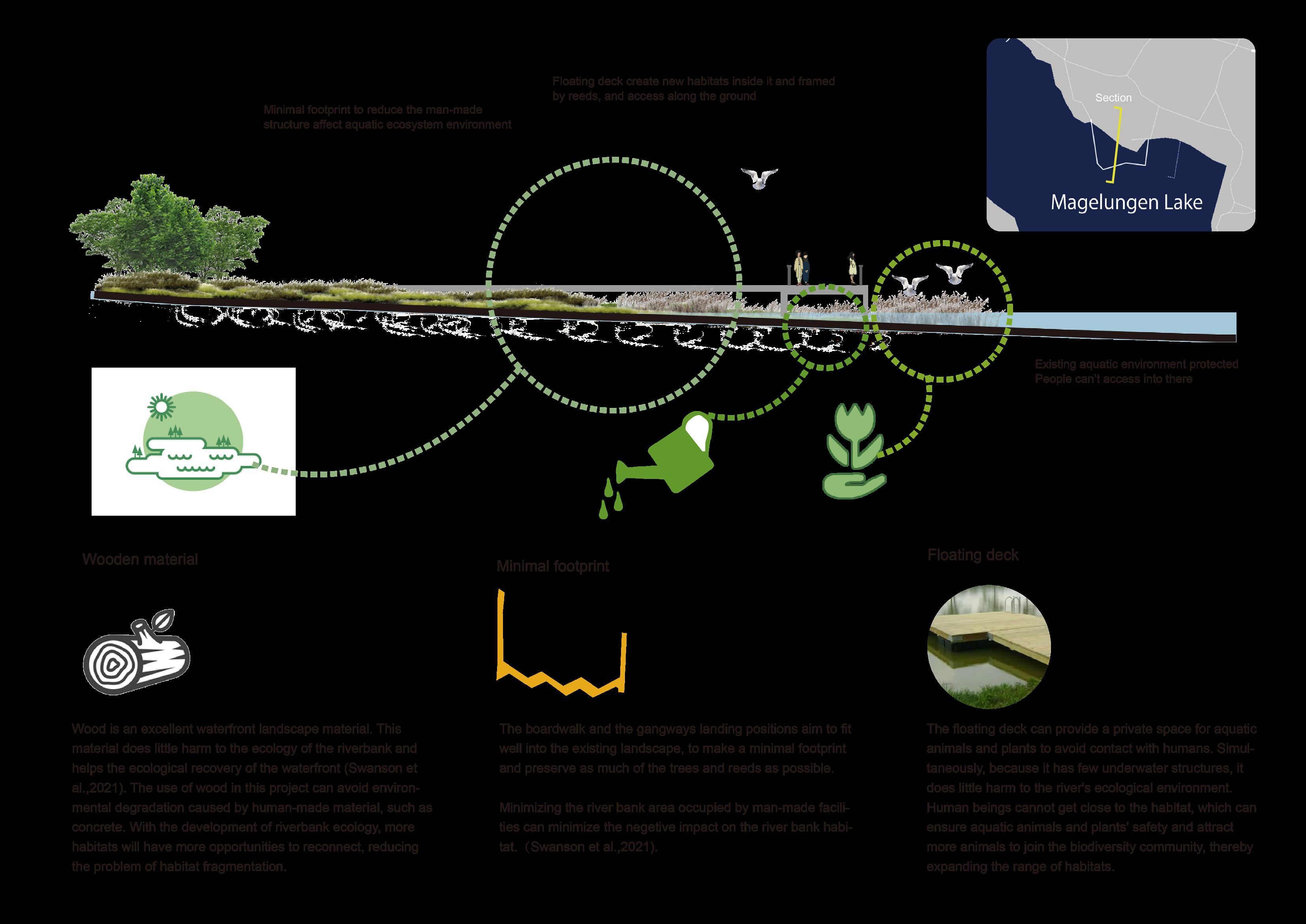
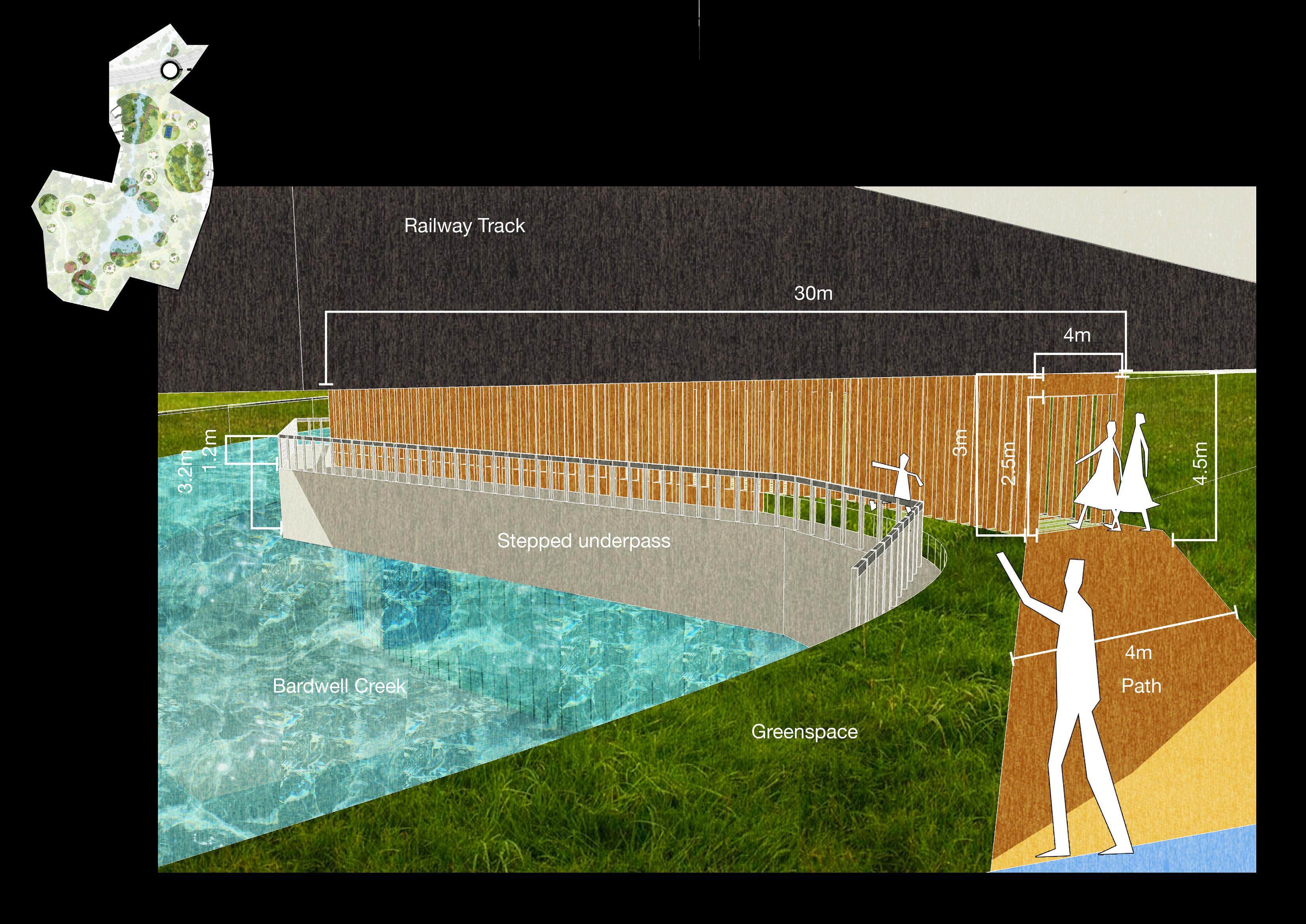
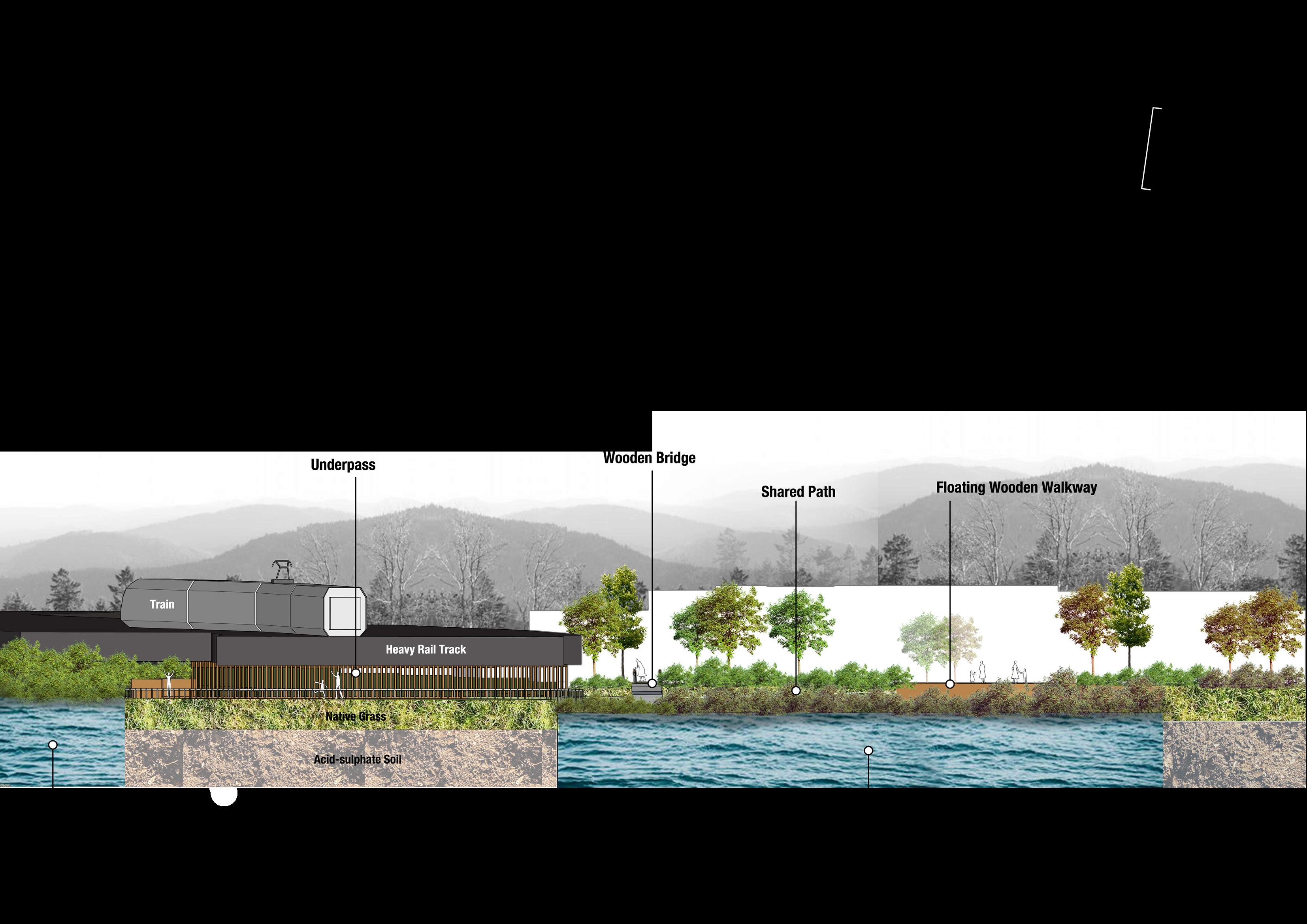
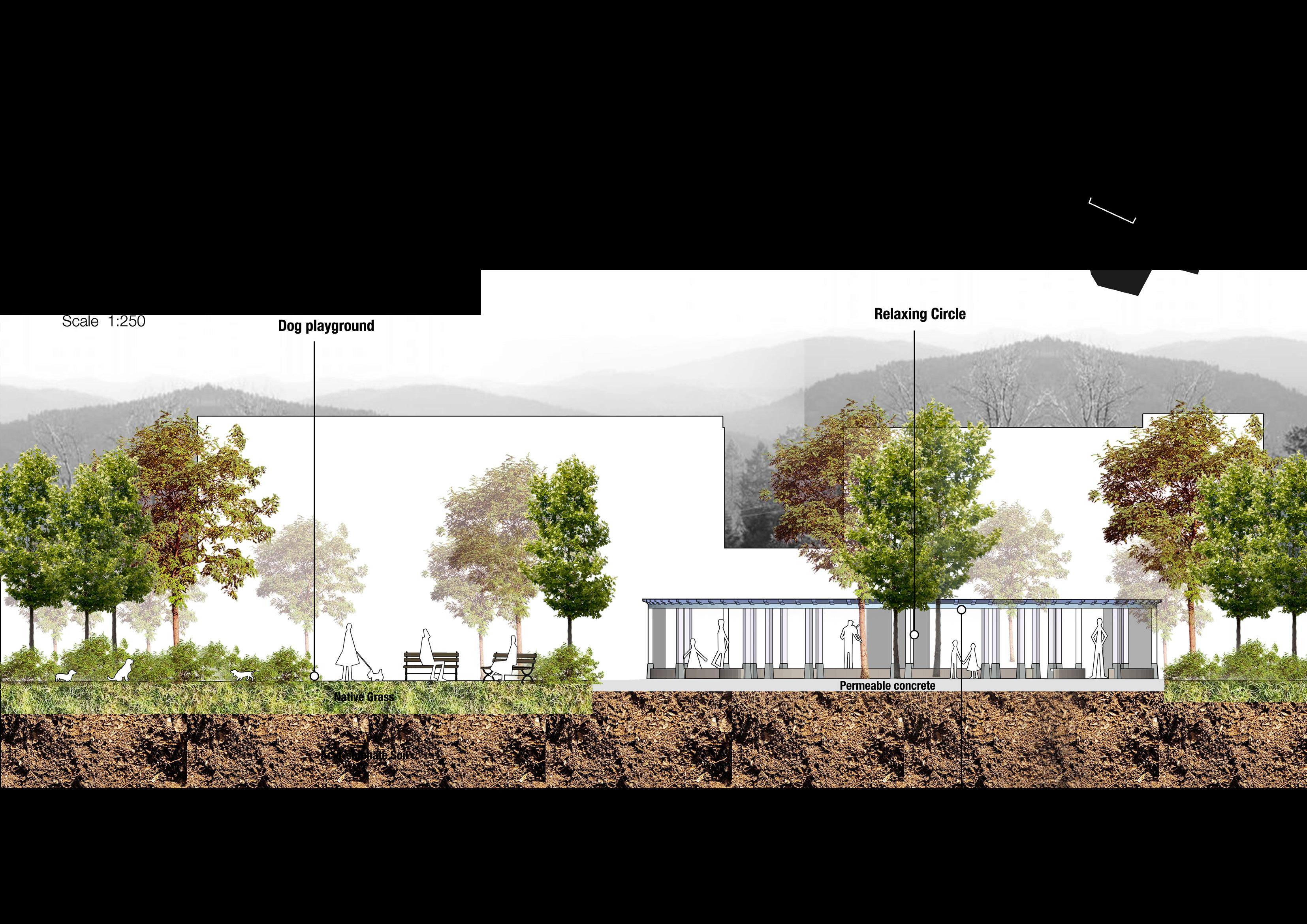
Farsta Lakefront Boardwalk
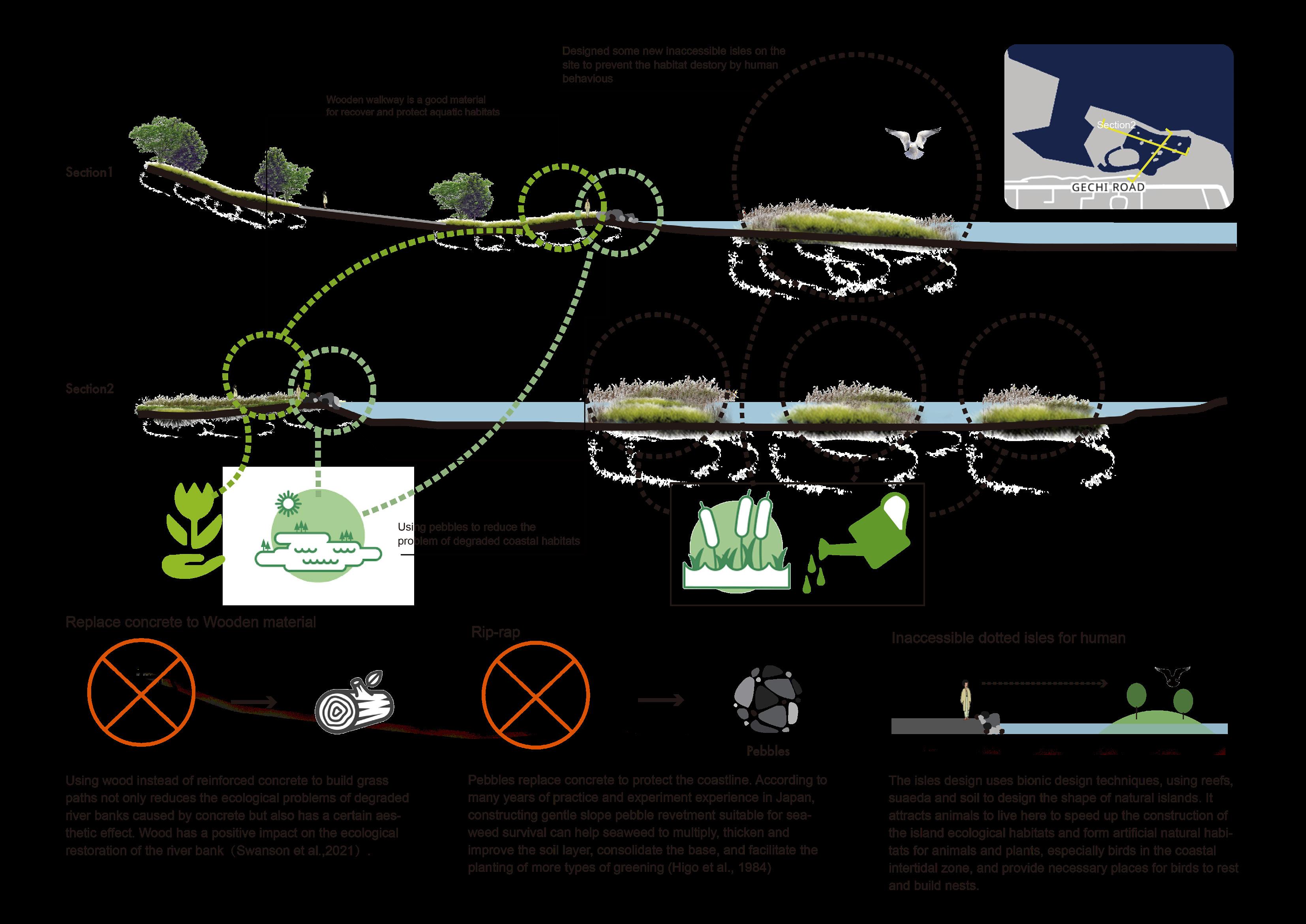
The Dotted Isles Lake and Eco-friendly Rip-Rap Wald.Berlin.Klima. – Exhibition in the Forest
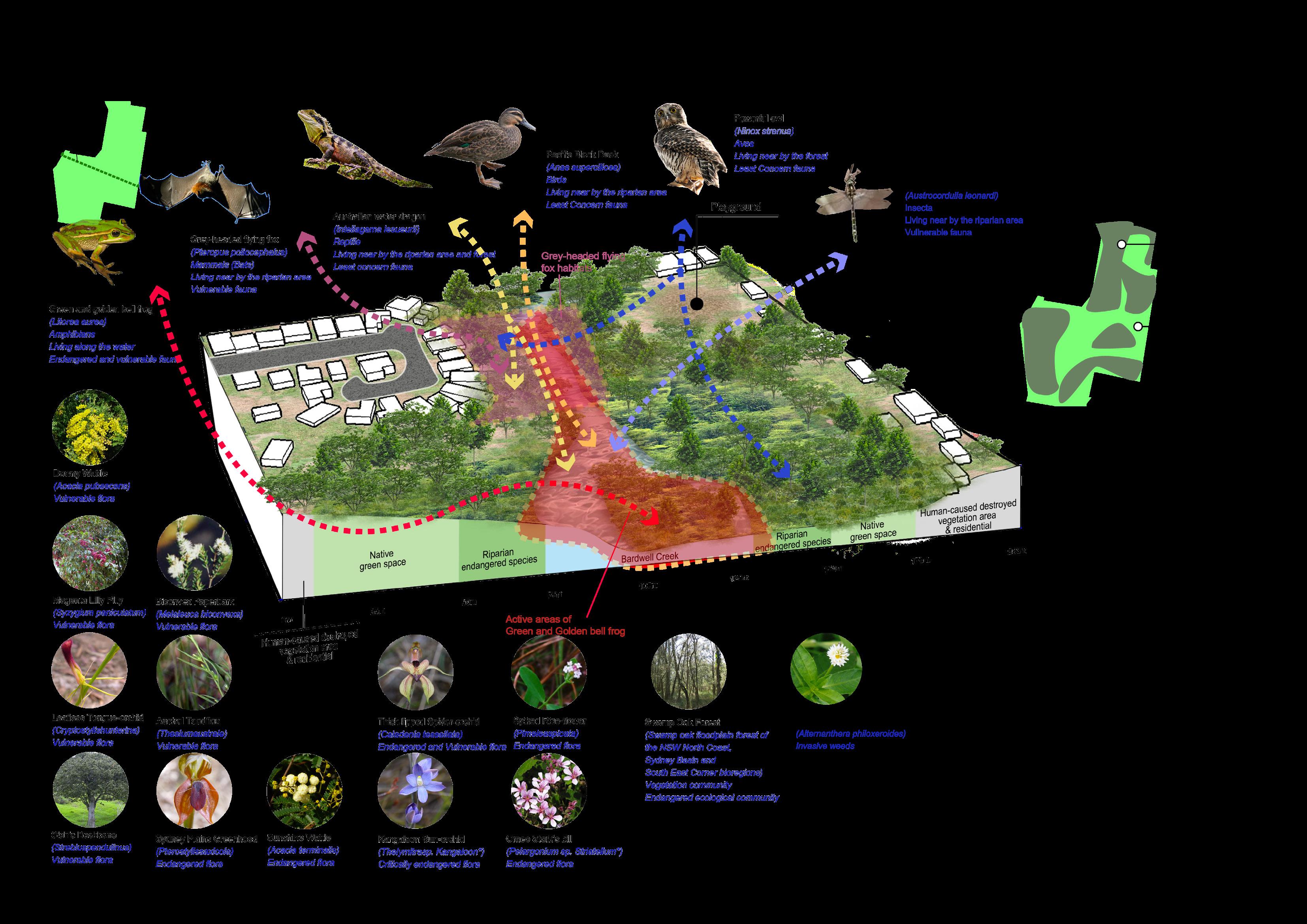
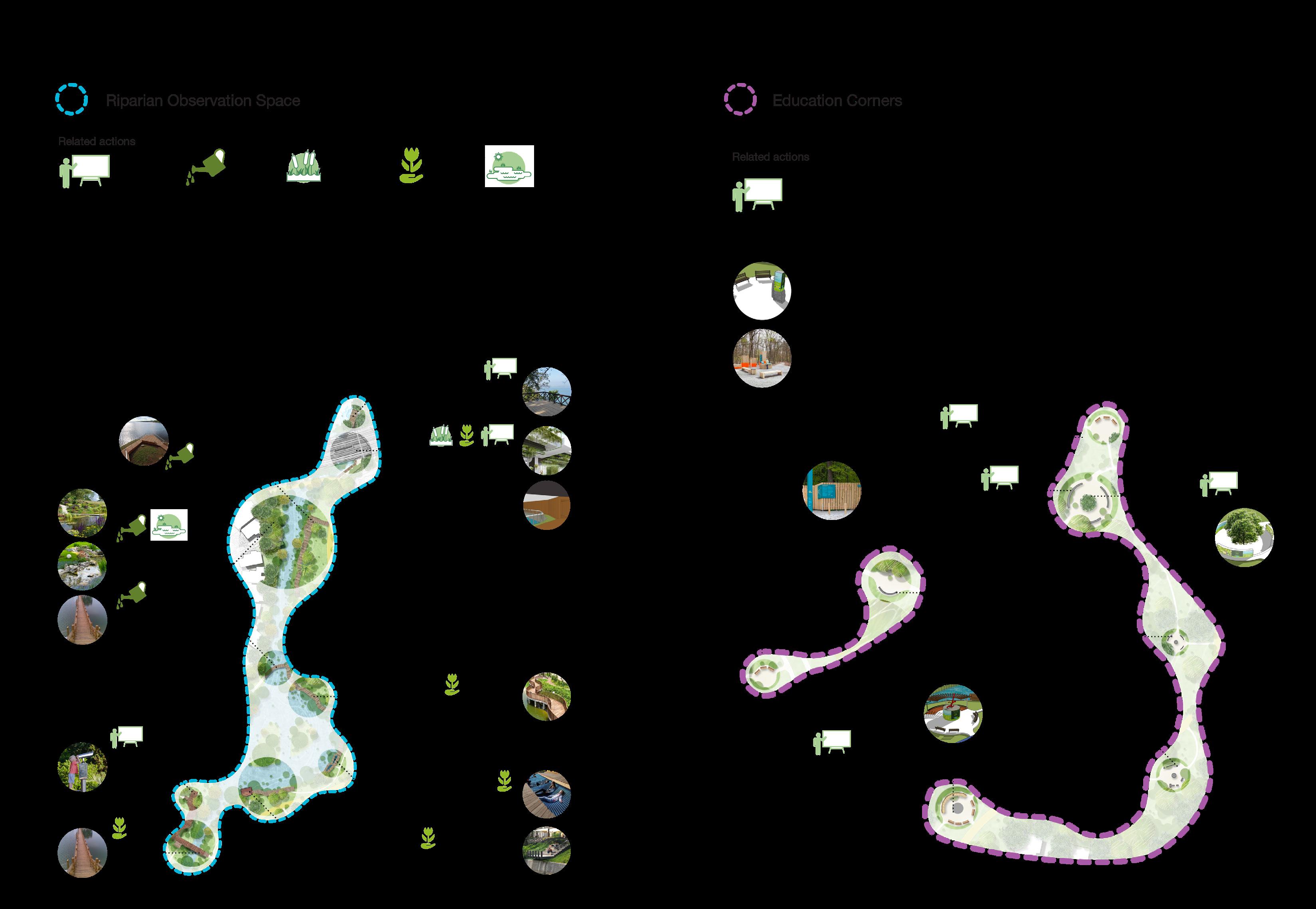
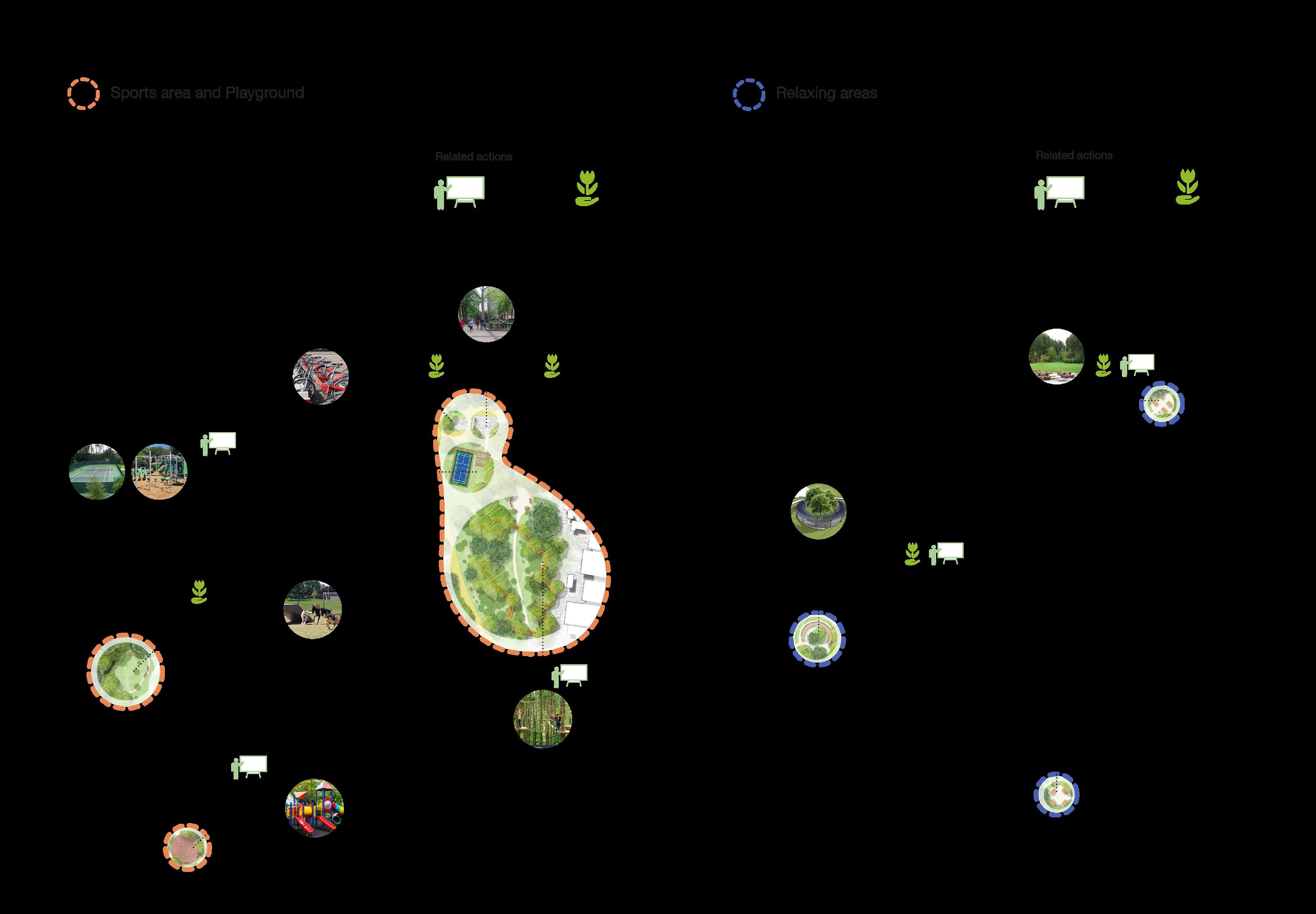
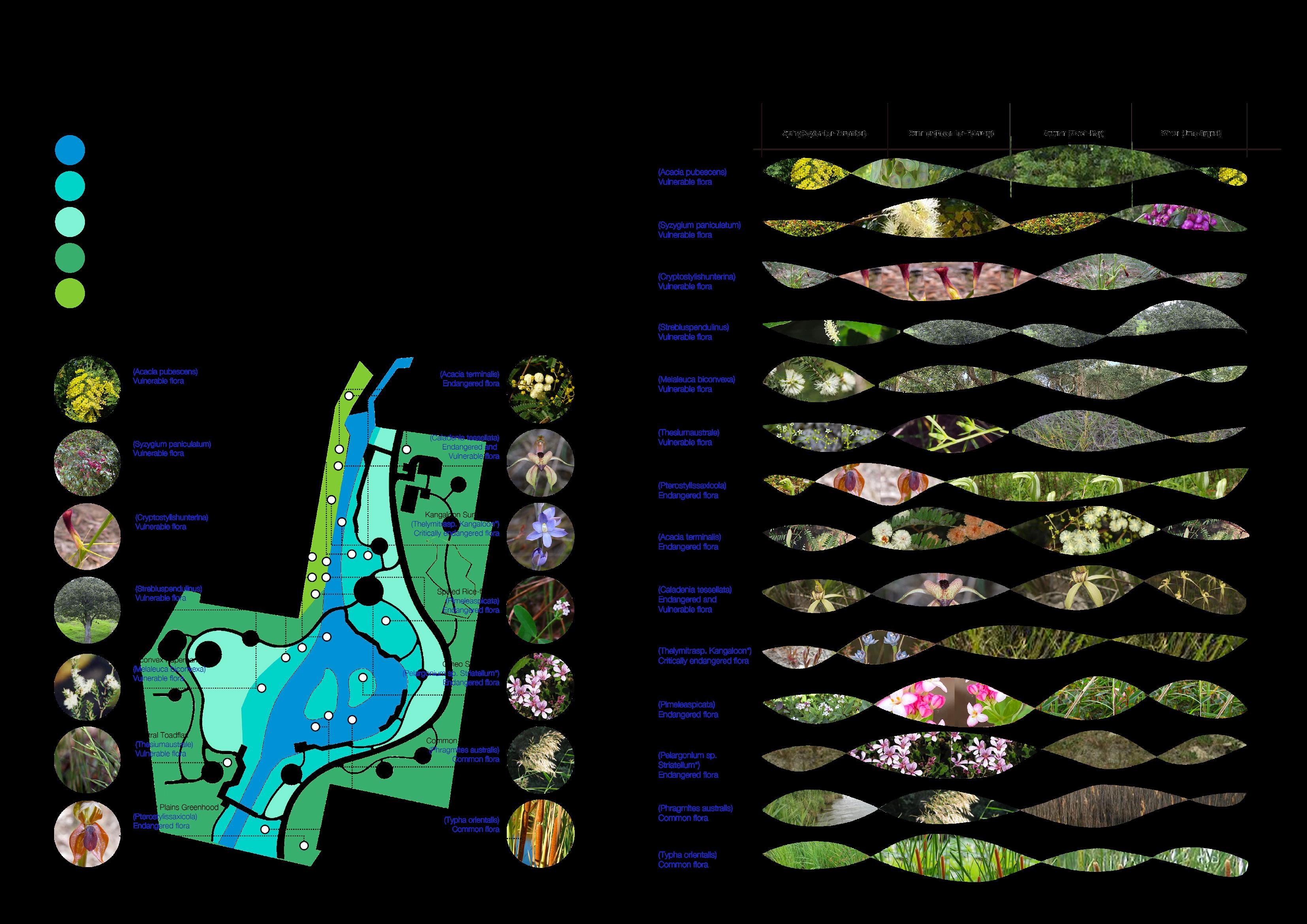
3 Relationship with Research Site
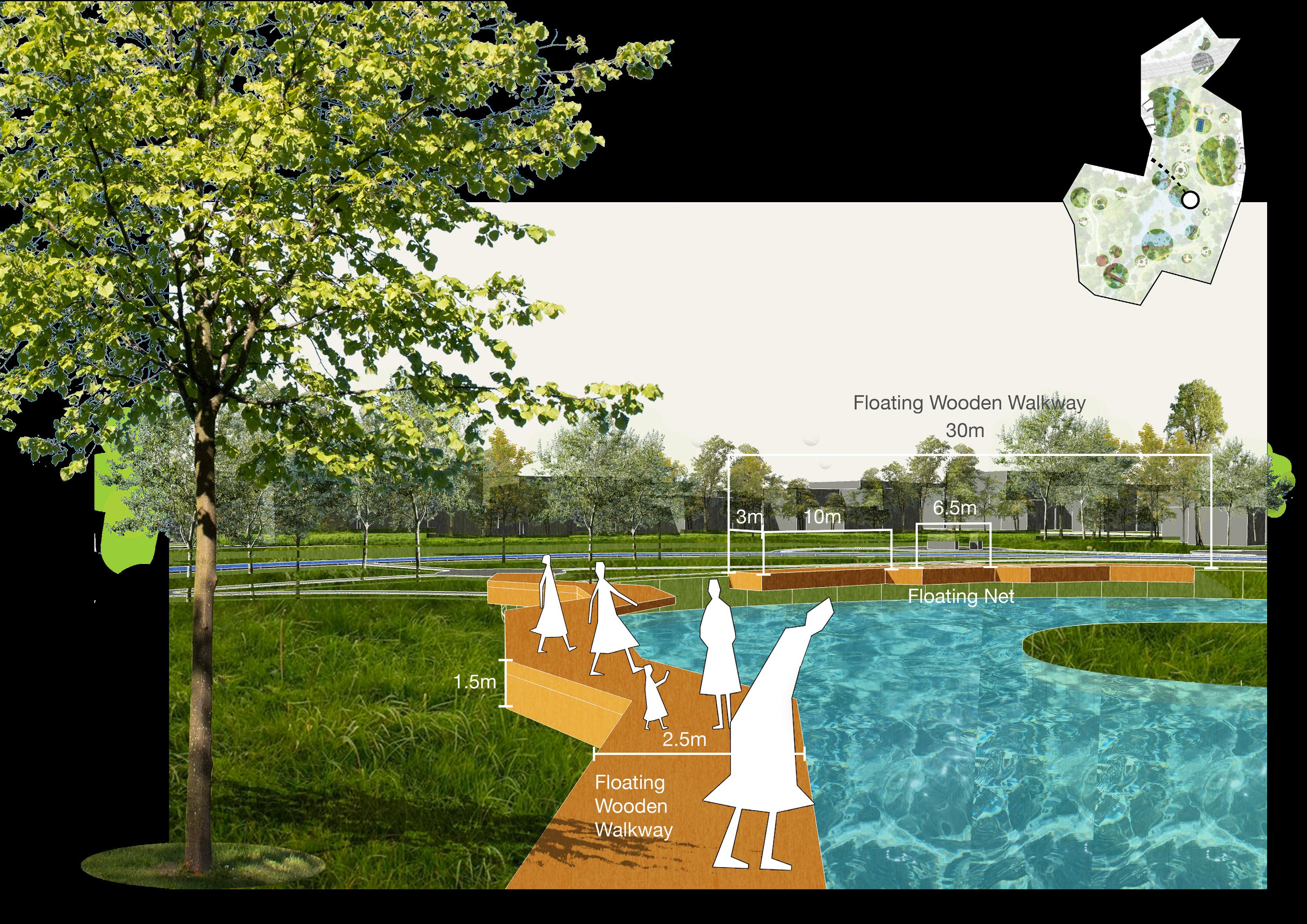
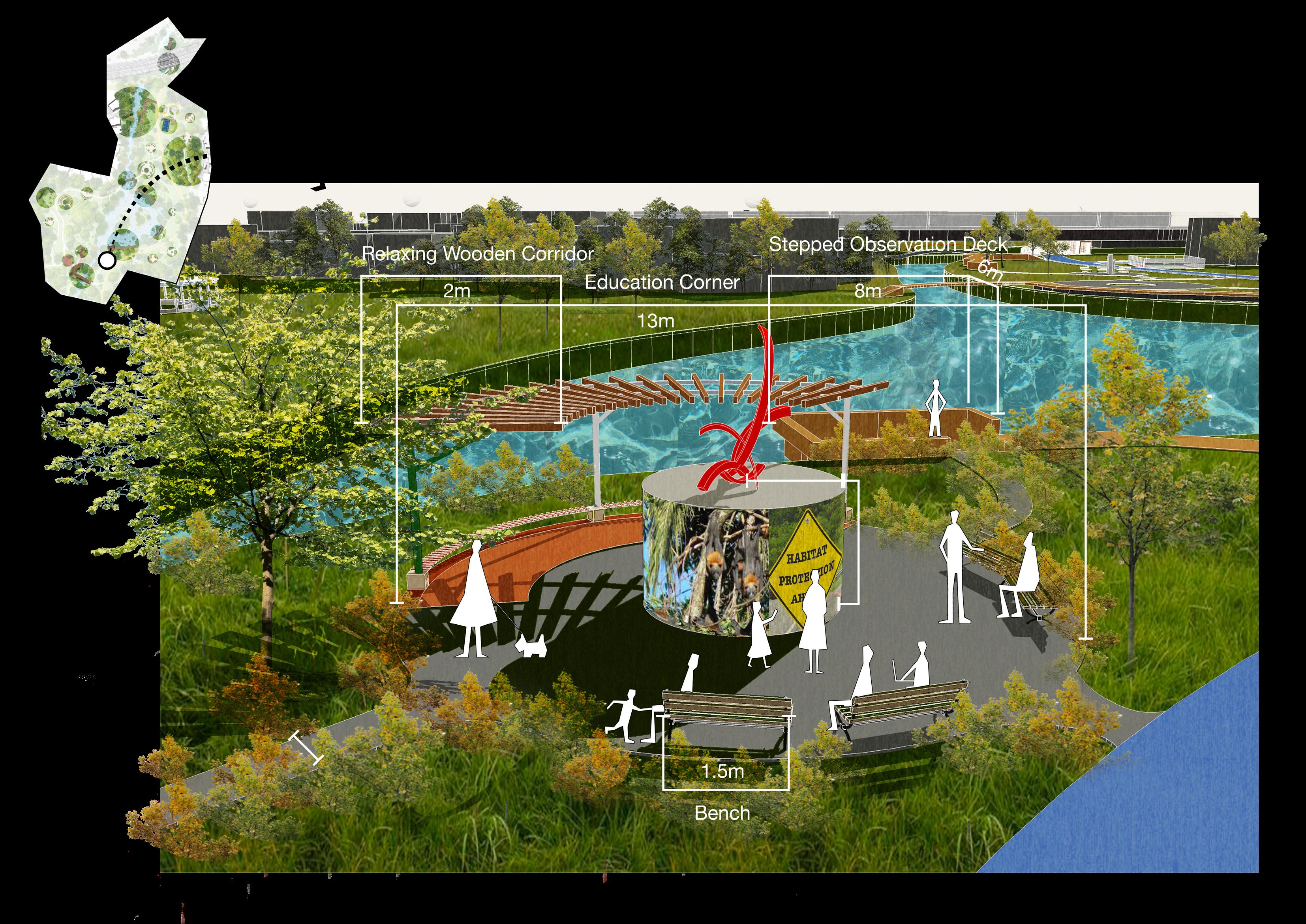
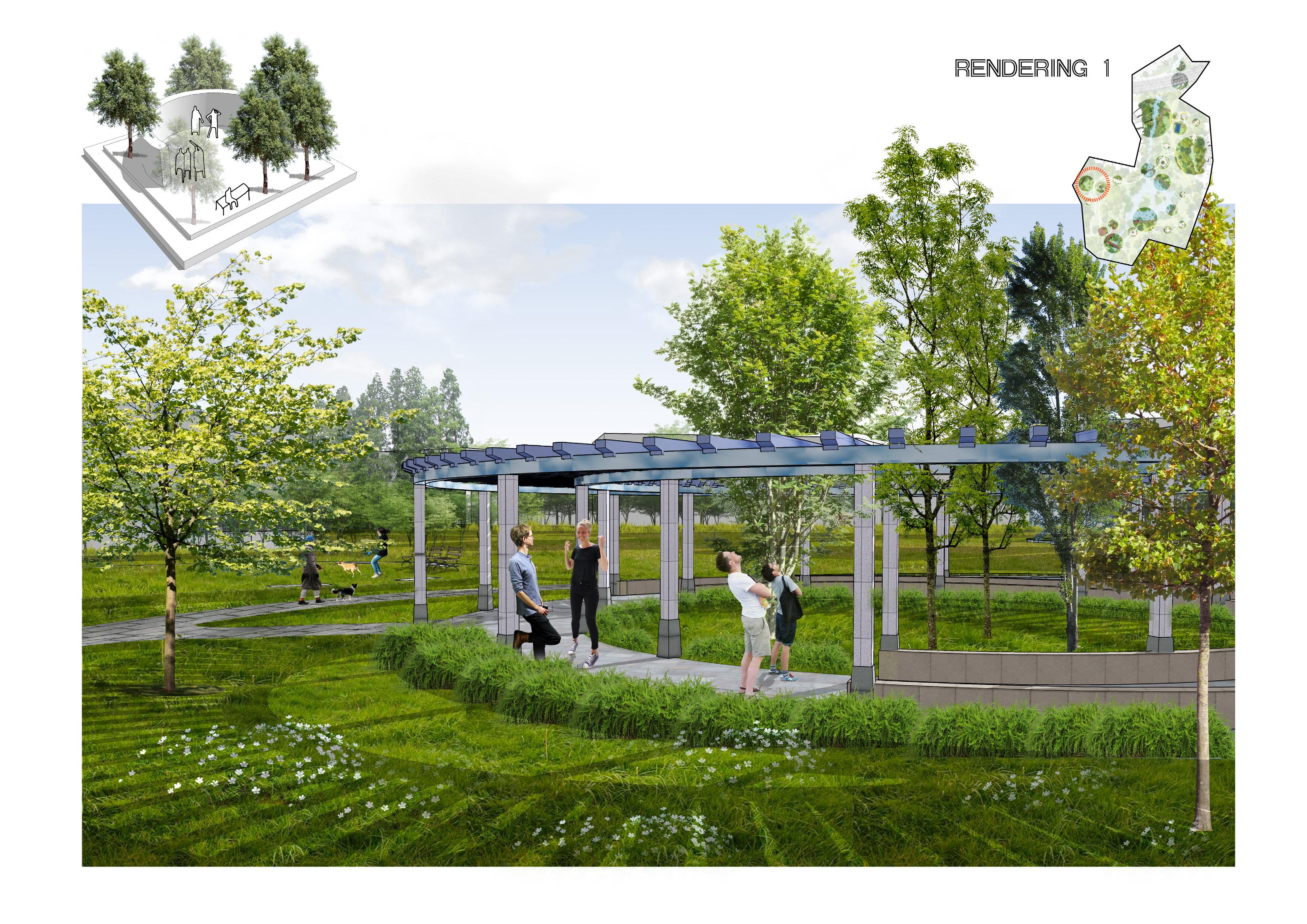
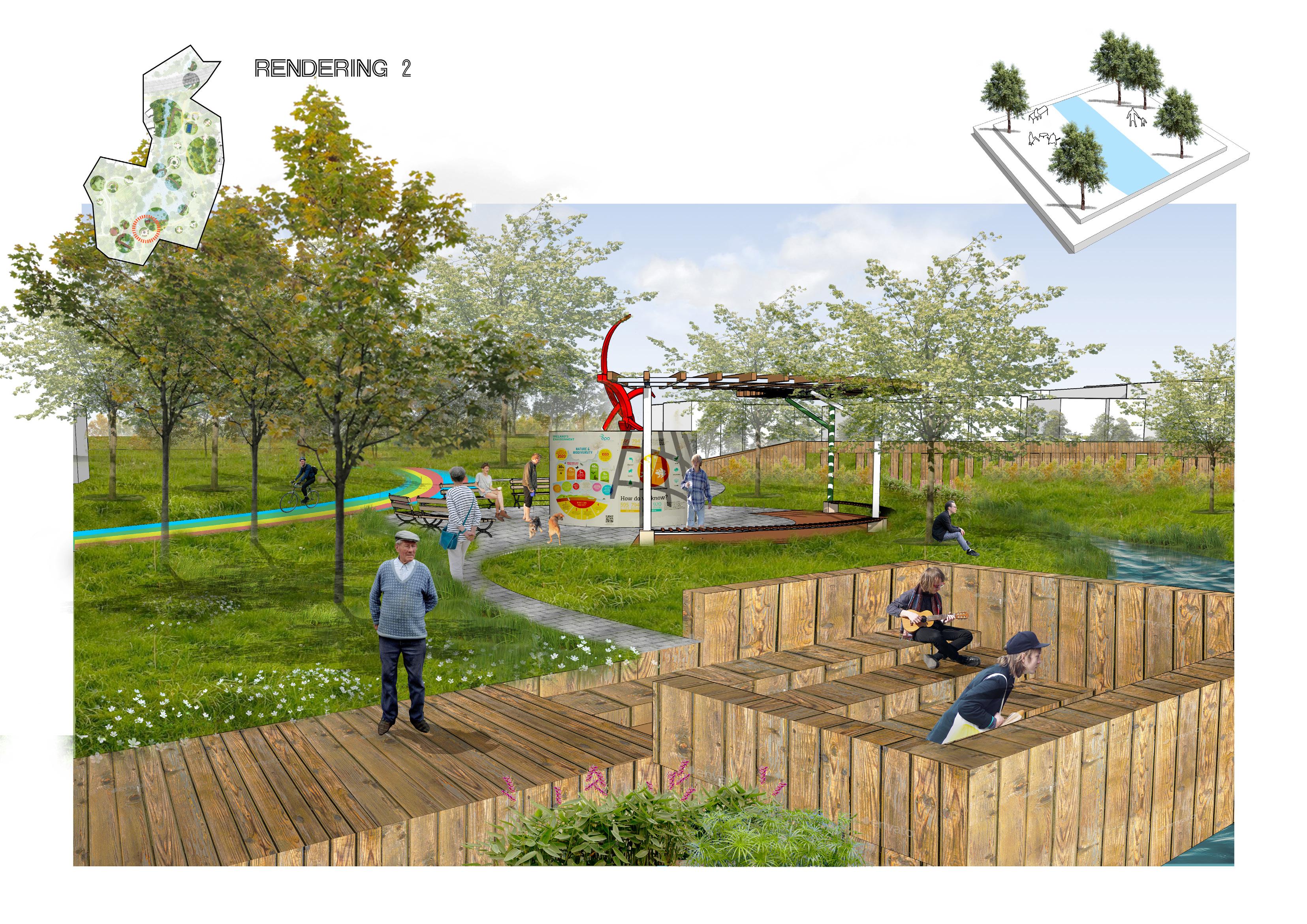
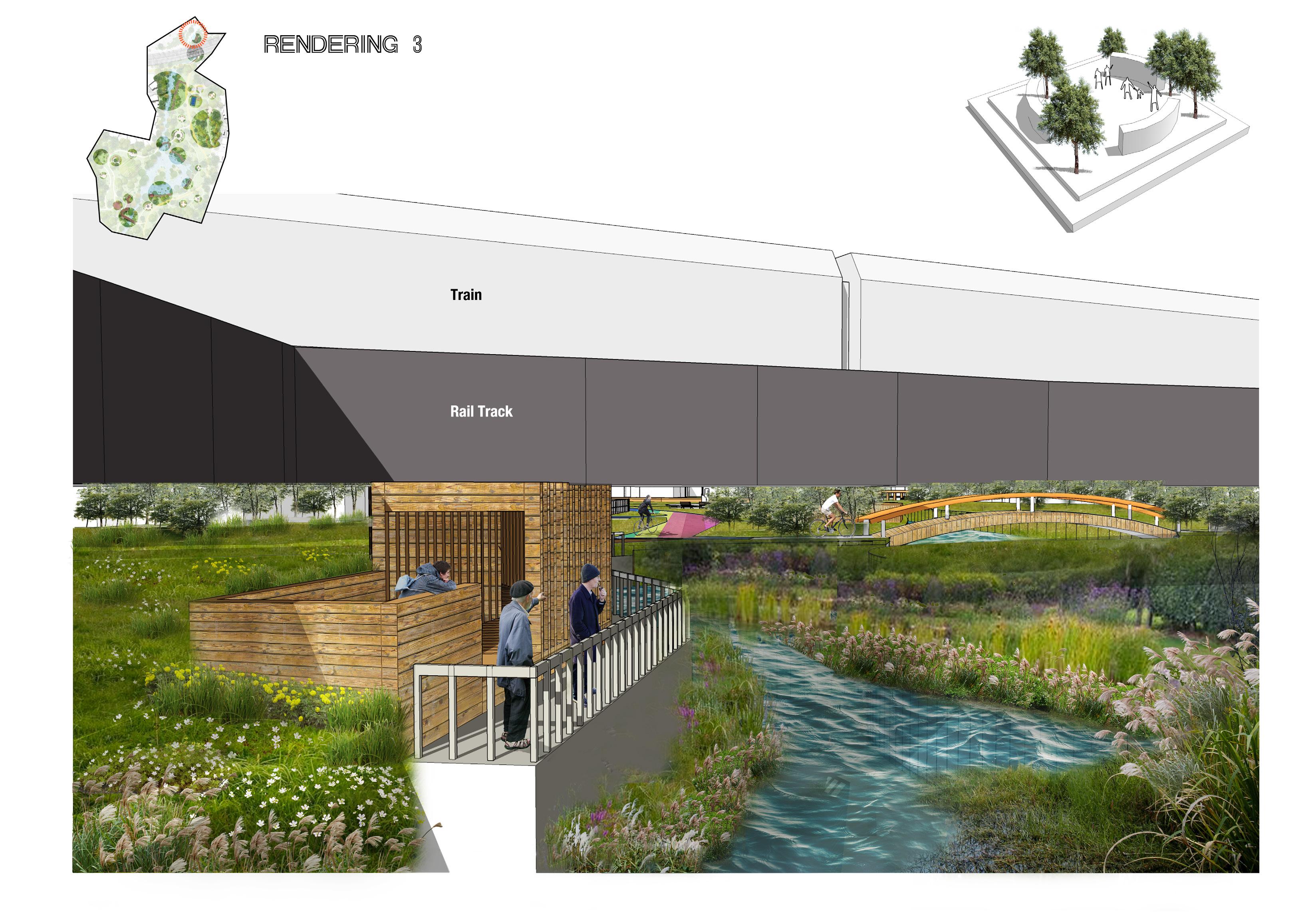
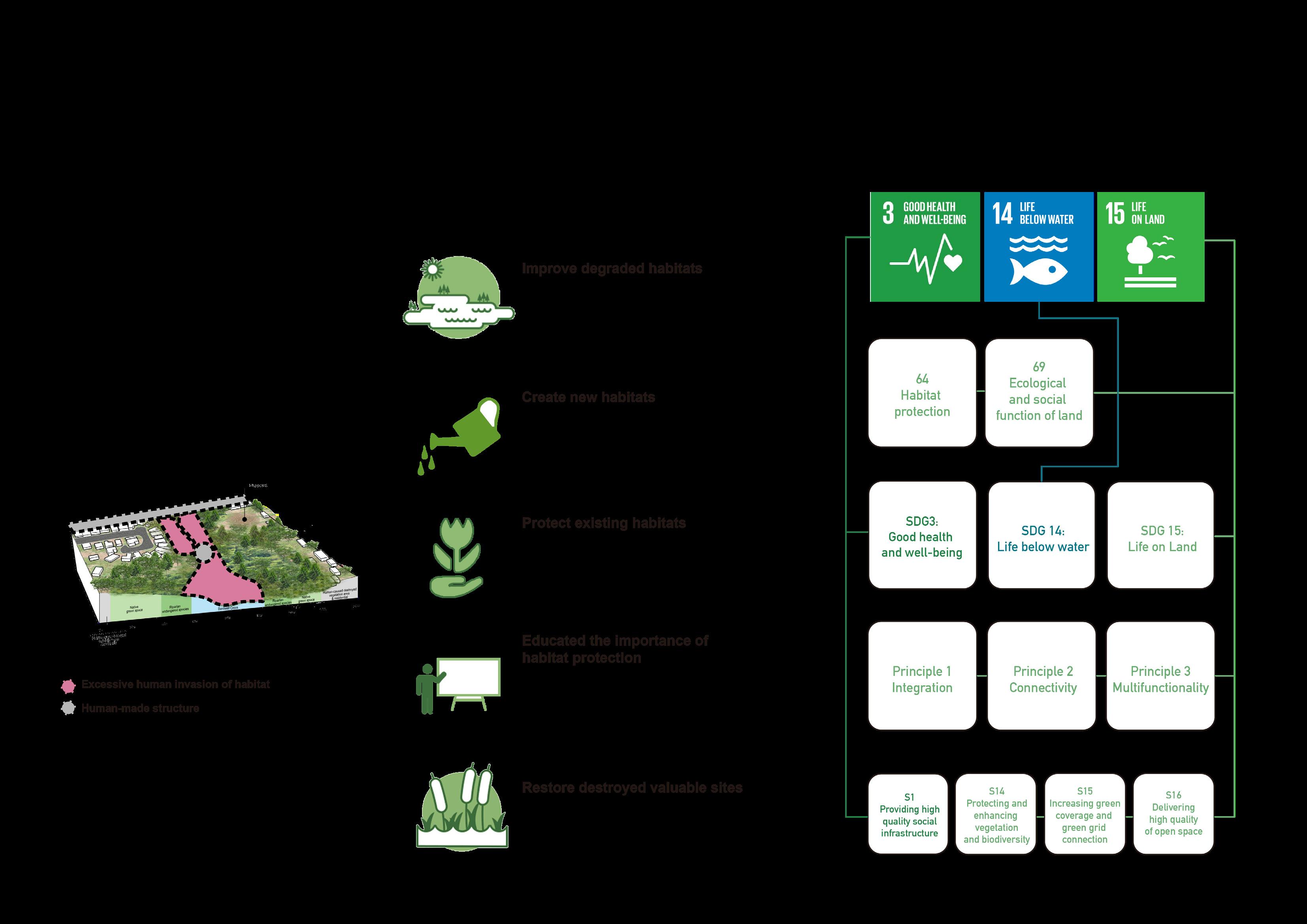
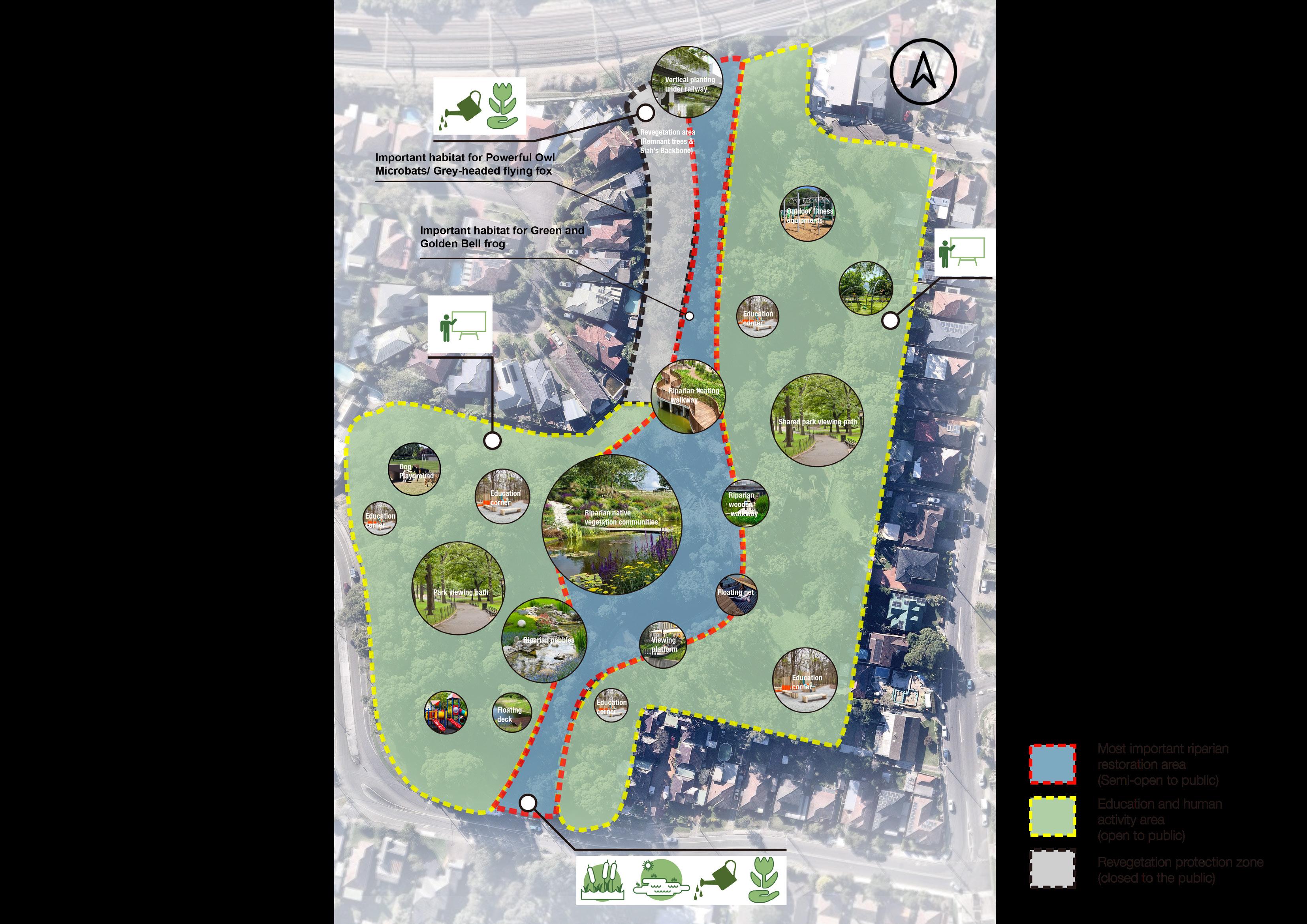
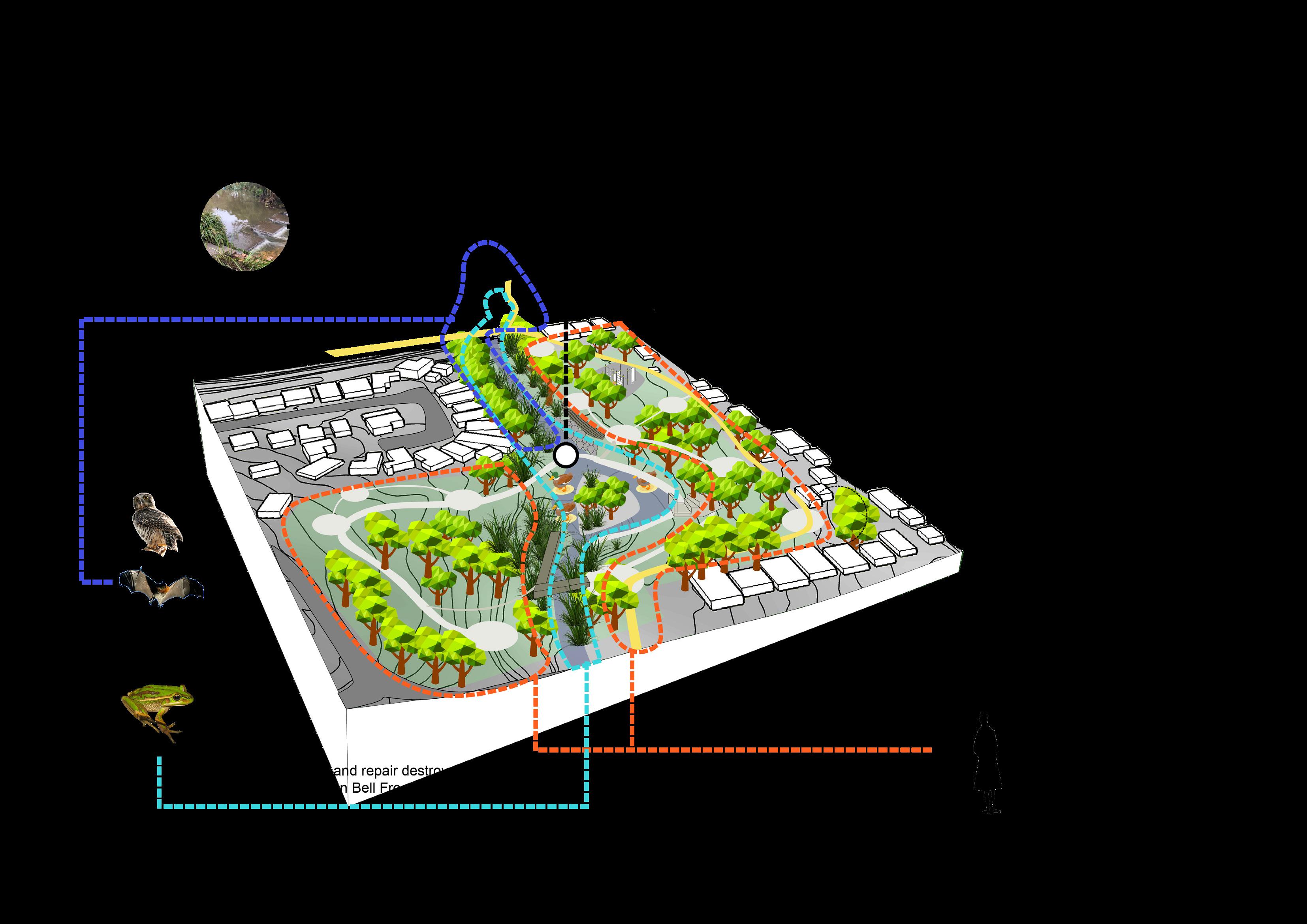
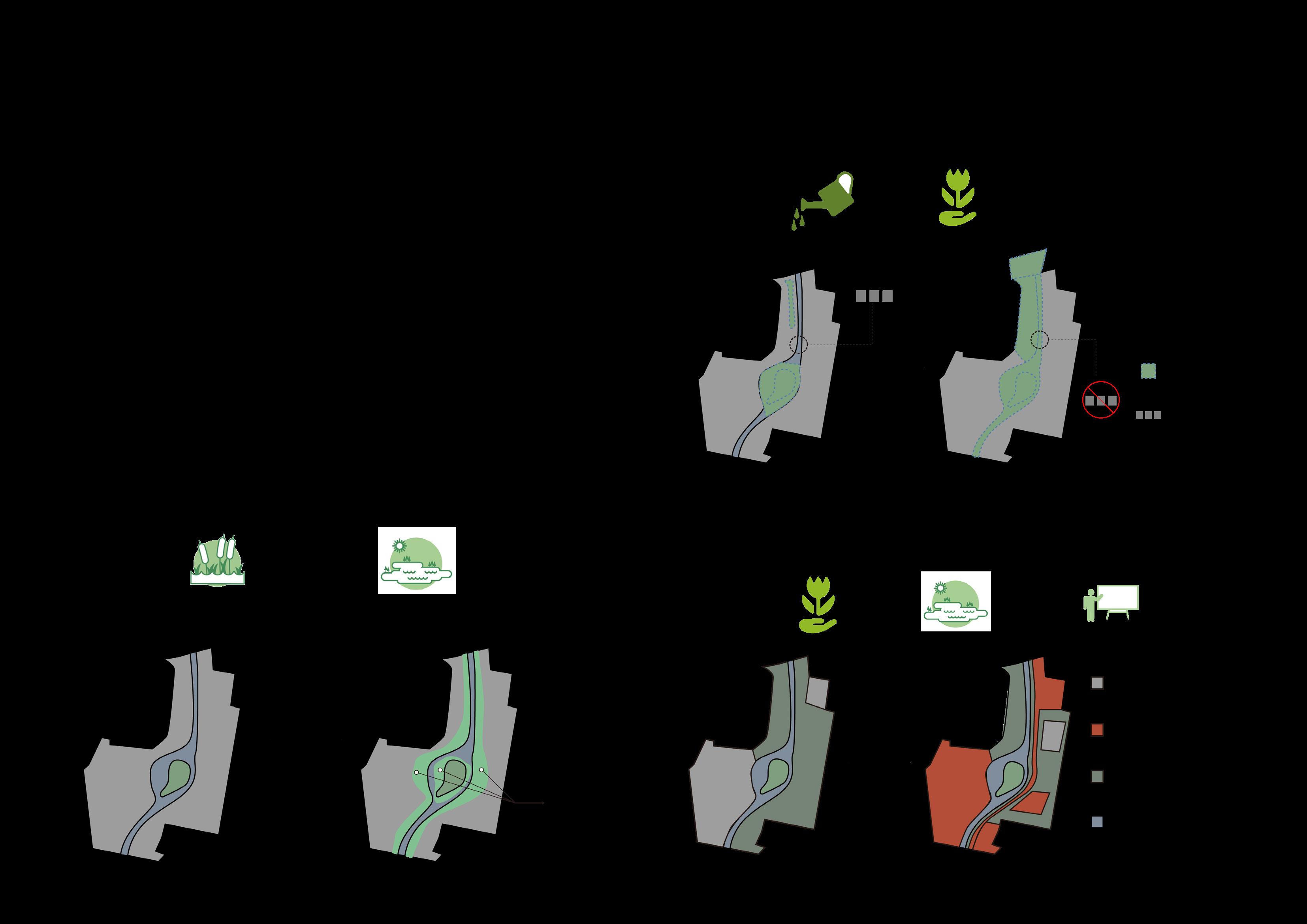
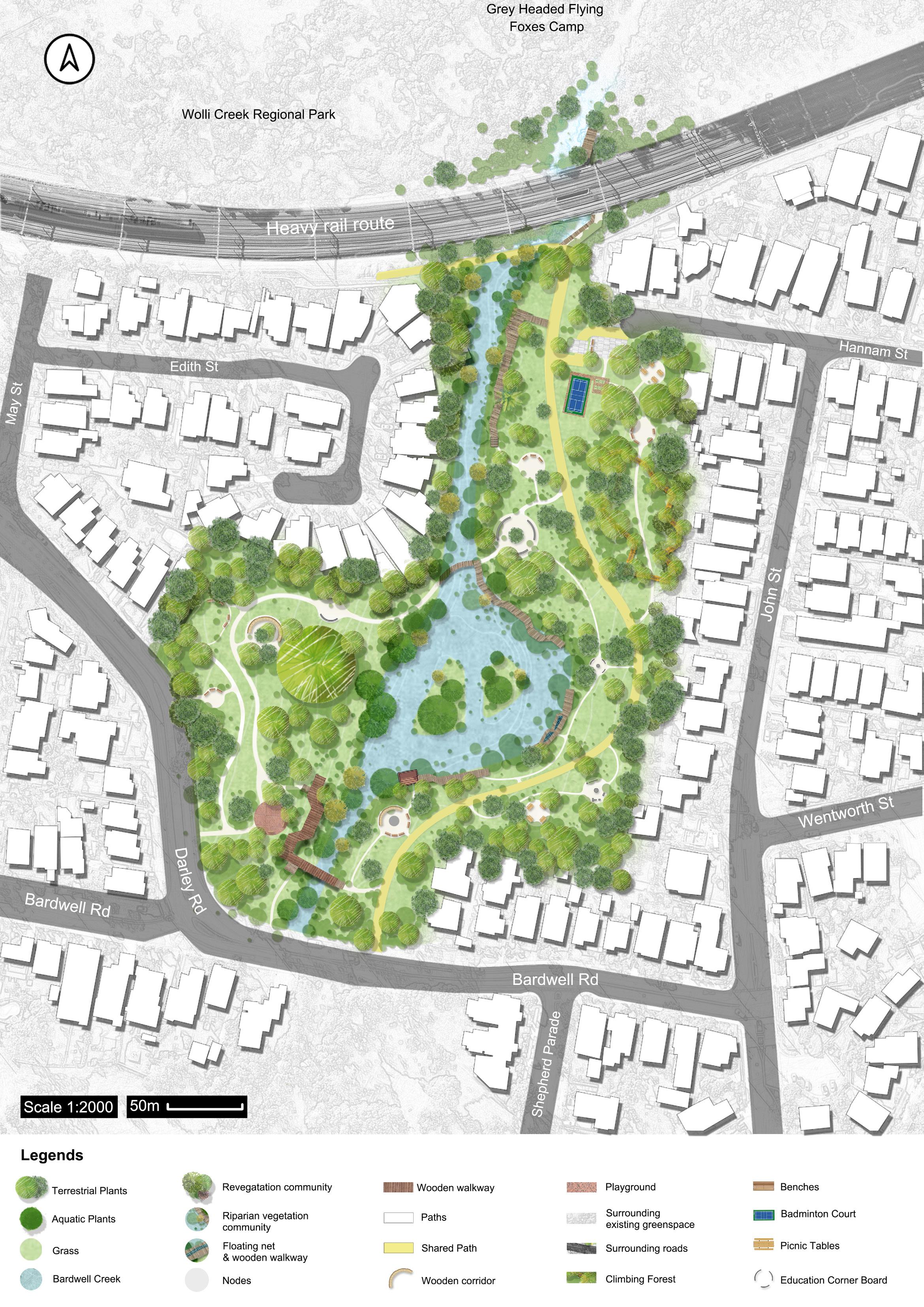
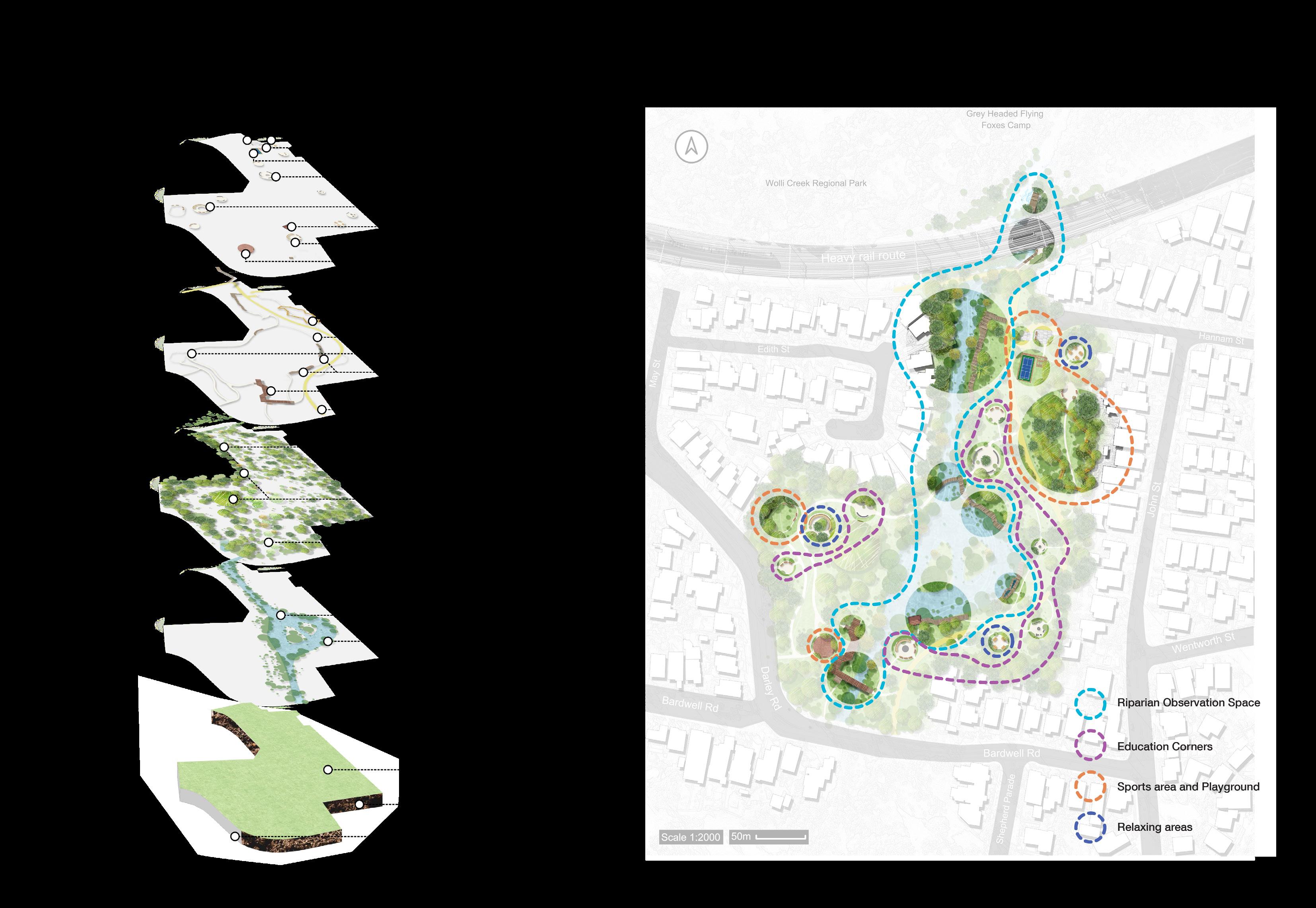
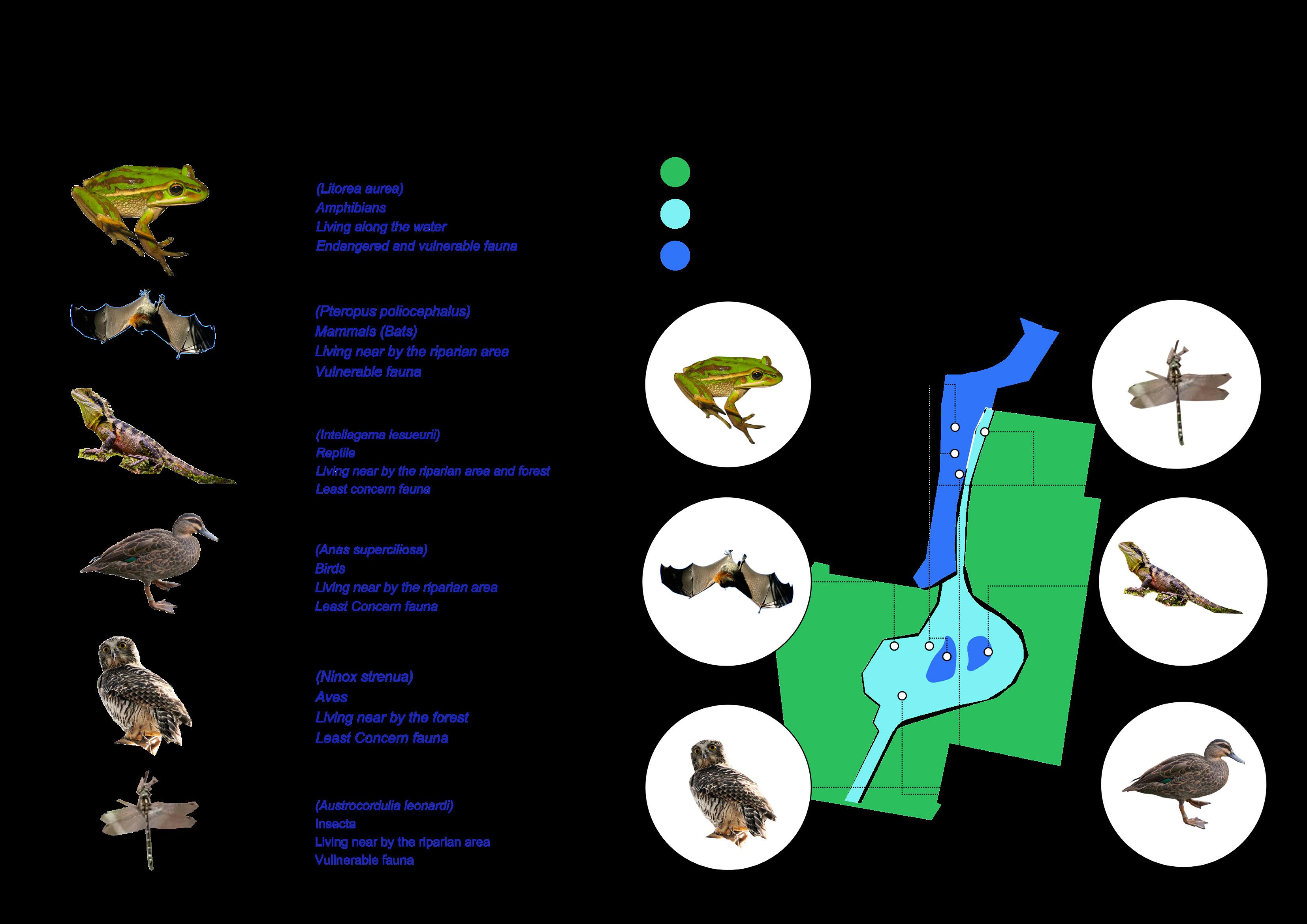
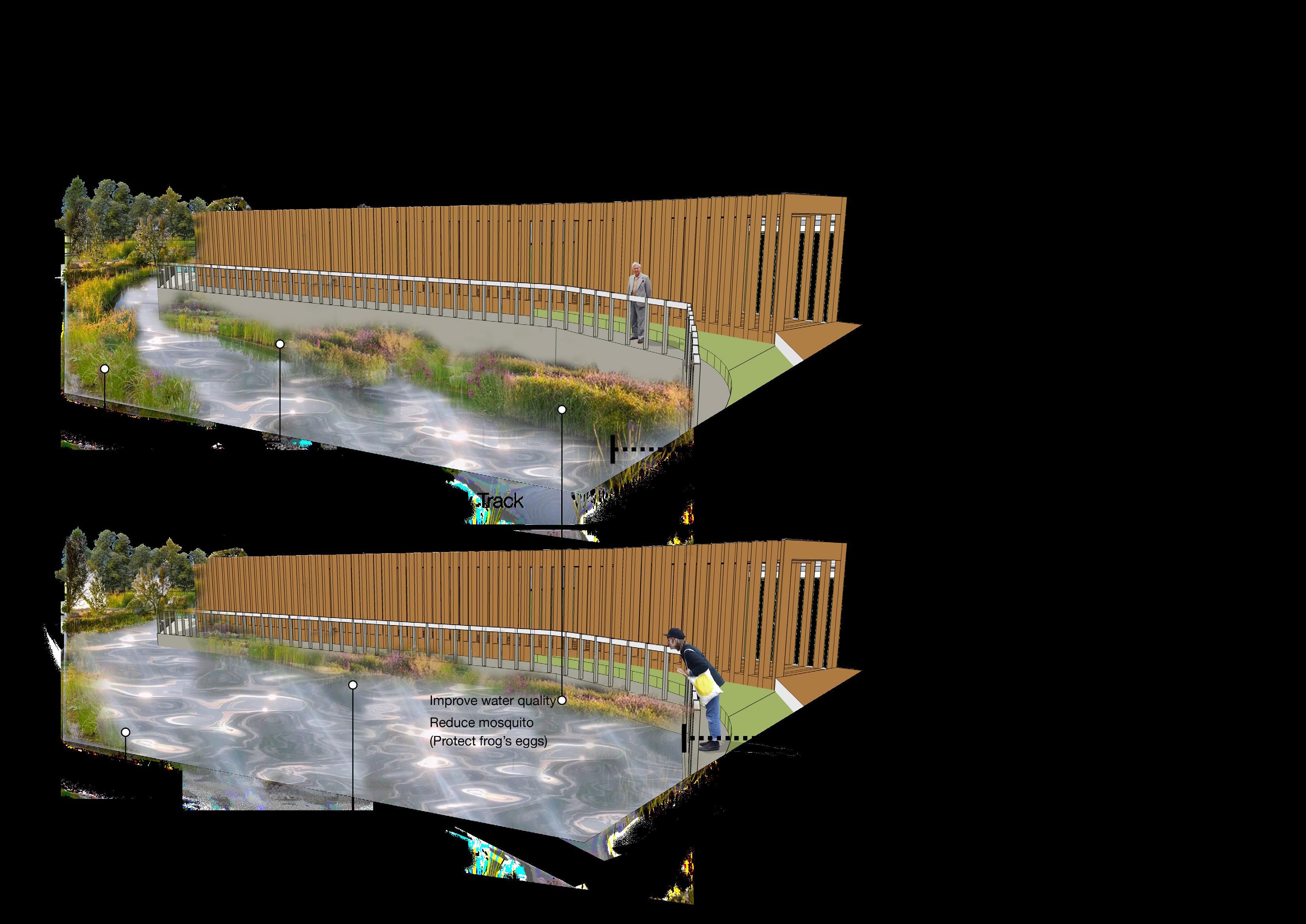
Improve degraded habitats
Create new habitats
Protect existing habitats
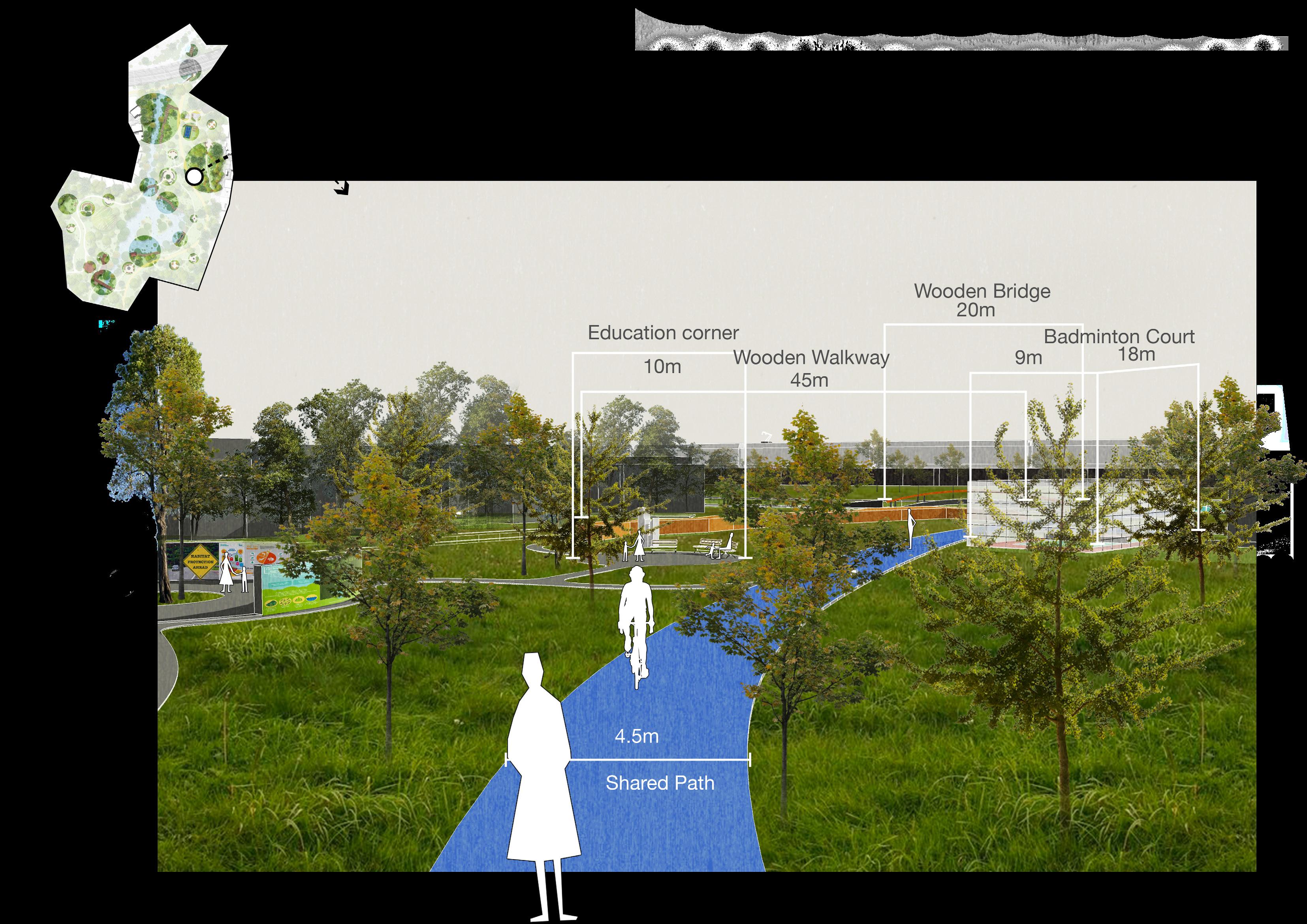
Educated the importance of habitat protection Restore destroyed valuable sites